
This is the 9th part of our seminar “Intellectual Property in Japan (Patent right)”.
“License” will be explained in an easy-to-understand manner with slides.
☆ ☆ ☆
As a method for developing new product, one can joint with universities or companies which hold patented invention.
In that situation, the developer need a patent to be licensed.
In this part, “license” will be described.
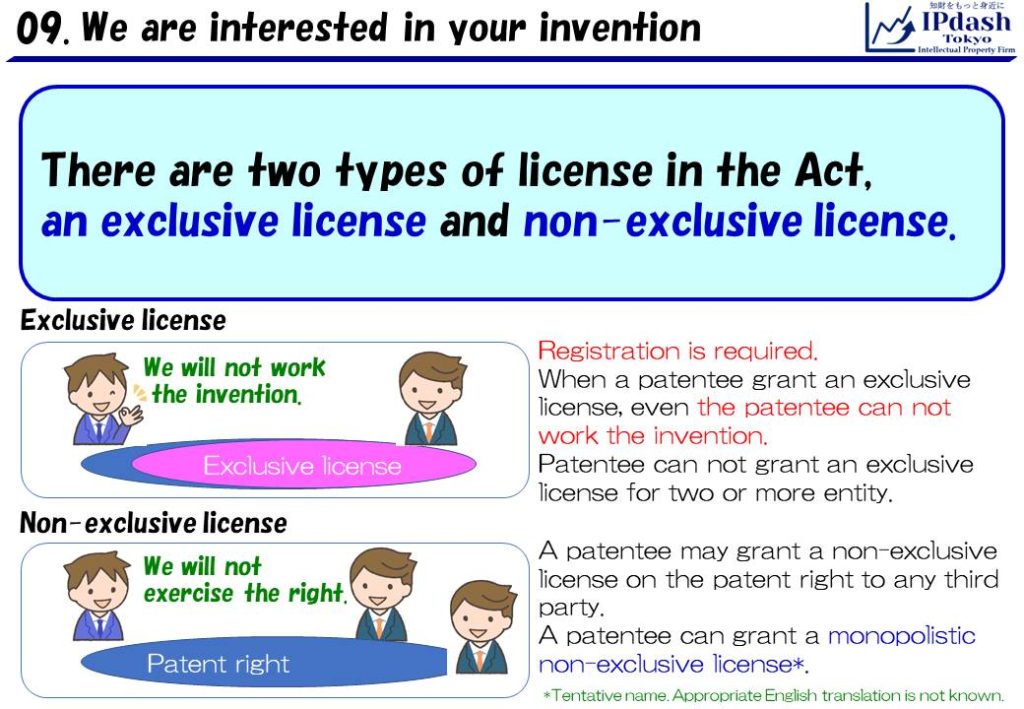
There are two types of license in the Japan Patent Act, an exclusive license and non-exclusive license.
What is a difference between an exclusive license and non-exclusive license?
☆ ☆ ☆
Exclusive license in the Japan Patent Act may not be heard so much.
However, the license is a strong right.
When a patentee grant an exclusive license, even the patentee can not work the invention.
For example, company A developed an engine alpha and obtain a patent of the invention.
Then, company A grant an exclusive license (in the Japan Patent Act) to company B.
In this case, even patentee, company A, can not work (produce, use, etc.) the engine as a business.
☆ ☆ ☆
However, exclusive license (in the Japan Patent Act) is not utilized actively.
It may be because that granting an exclusive license (in the Japan Patent Act) need a registration to Japan Patent Office, and the registration is published (a third party can browse a content of the registration).
Companies seem to avoid such a situation because they want to keep a secret of the content.
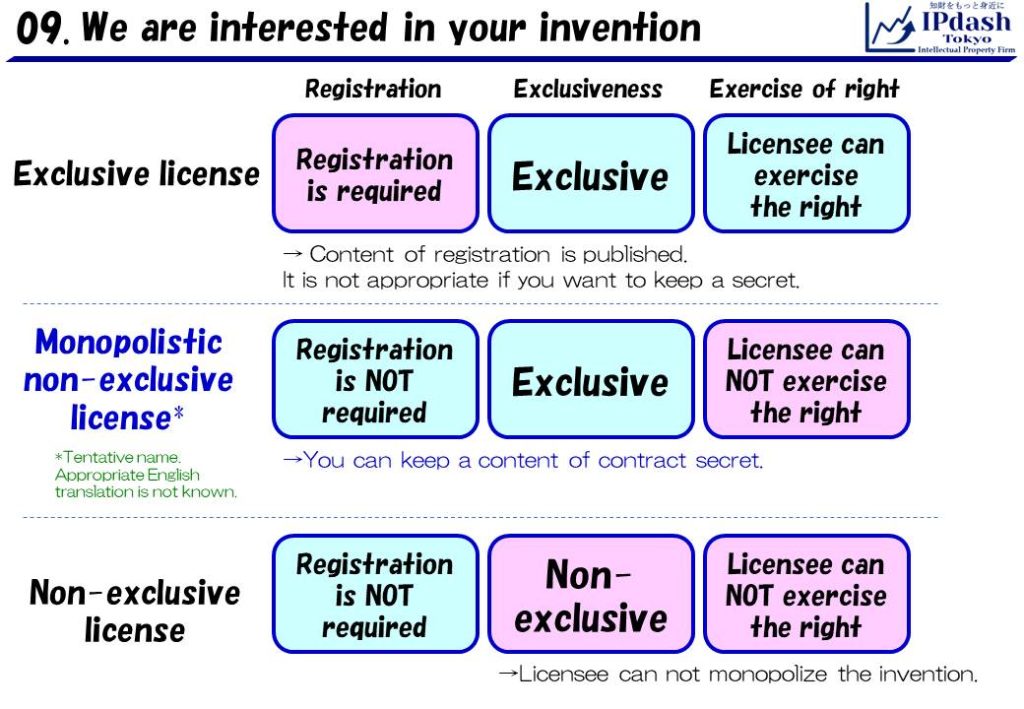
Therefore, when companies need to license their patent for someone, non-exclusive license, especially “monopolistic non-exclusive license*” seems to be utilized.
“Monopolistic non-exclusive license” is NOT the license written in the Japan Patent Act.
“Monopolistic non-exclusive license” is a kind of non-exclusive license, and the exclusiveness is secured by the contract between a licensor and a licensee.
A licensee can monopolize the patented invention, and they can keep a secret about their contract.
*NOTICE: “monopolistic non-exclusive license” is a tentative word. Appropriate English translation is not known.
☆ ☆ ☆
Let’s think on the situation according to the example above.
Patentees think that they can grant a license of engine alpha, but they want to work the engine by themselves too.
How should do the patentees?
The answer is simple.
Non-exclusive license works well.
Patentees can produce or use the engine too.
They don’t need the discloser of their secrets.
It’s all for “exclusive license” and “non-exclusive license”.
☆ ☆ ☆

I’d like to wrap up with a summary of this part.
1. There are two types of license, an exclusive license and non-exclusive license.
2. A patentee can grant an exclusive license such as a monopolistic non-exclusive license, or exclusive license.
☆ ☆ ☆
That’s all for Part 9 (License).
IPdash Tokyo Intellectual Property Firm (Japan)
(To Part 08) (To Part 10)
(To List)
